What is a cyber-attack vector? | Avoid these 10 common attack vectors

What is a cyber-attack vector? | Avoid these 10 common attack vectors
Cyvatar | 02/08/2022Attack vectors are vulnerabilities in target systems, networks, or cloud environments that are exploited by cybercriminals to gain unauthorized access.
The intention behind gaining such access could be to either manipulate or extract company data, gain personal identification information, access further system vulnerabilities, or take control of resources.
Relevance of Attack Vectors in Cyber-incidence?
Attack vectors are touchpoints through which cyber-crime can be initiated. The attacks on these touchpoints can be broadly classified into Active and Passive attacks.
While the end objective of both types of attacks is similar, what sets them apart is the level of exploitation of the vulnerability.
Difference between Active Attacks and Passive Attacks
| Active Attacks | Passive Attacks |
|---|---|
| Leverage the vulnerabilities in the system while affecting the system’s operation and resources. | Leverage the vulnerability in the system to gain unauthorized access but do not affect the system operation and resources in this process. |
| These are easily identified as and when it happens. | Most often passive attacks take a long time to be identified, hence risking the system to future Active Attack Exploits. |
| These attacks are due to inherent weakness in the said system brought about usually by either misconfiguration, ransomware, the man in the middle attacks, system and software errors. | These attacks are mostly due to the weakest link in the cybersecurity of the organization. It happens via visiting phishing sites, clicking unsafe links, etc. |
| This affects the integrity and availability of the system. | It impacts confidentiality. |
The most common passive attack exploits are phishing emails, malicious insiders, and social engineering.
Whereas the most common active attack exploits are masquerade, modification of messages, repudiation, replay, denial of service, and session hijacking. There could also be a brand new active attack vector such as log4shell.
How are Attack Vectors and Attack Surface related?
While an attack vector could mean any of the vulnerabilities in the system, attack surface refers to all assets and resources that are vulnerable at any given point in time and could be attacked using any of the attack vectors.
To understand better– if we can consider our system or application to be a financial institution such as a bank, the attack vector would relate to all the vulnerabilities exposed to said bank at any given moment such as armed robbery or cyber-attack on bank servers or insider malpractice which could risk the resources it holds– in this case, the money stored in the bank physically– while attack surface would mean the total assets and resources that are available for exploitation to the potential criminal using the attack vectors.
The following chart explains the difference between an attack vector and an attack surface.
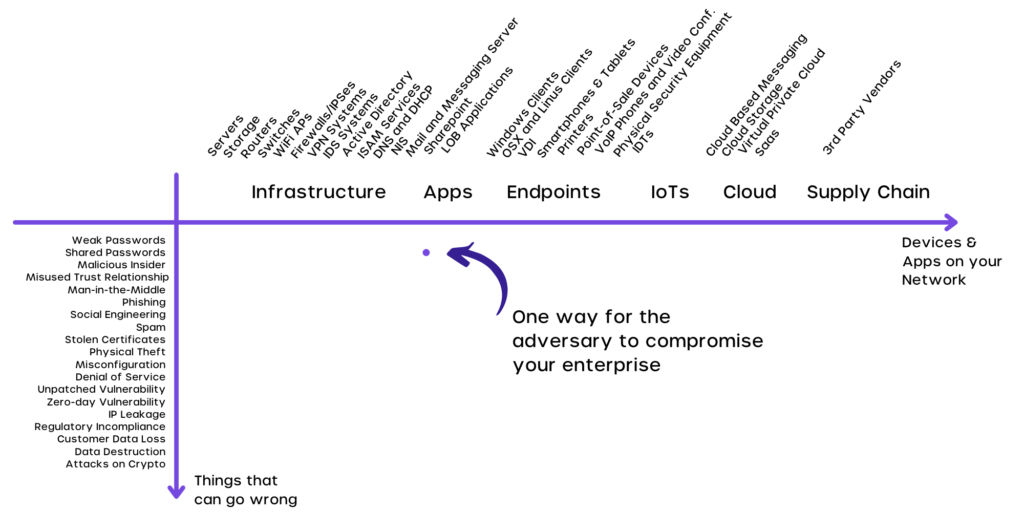
Simply put, an attack surface is 2 dimensional on a chart that includes all the attack vectors that could be used by an attacker and the assets of the system that are vulnerable to such attack vectors.
The following are the 10 most common Attack Vectors in Cybersecurity to guard against in 2022:
1. Compromised Credentials
Compromised credentials were the most common initial attack vector, responsible for about 20% of the breaches in 2021 and contributing about $4.37M in average cost to businesses in cyber incidents.
A common type of passive attack vector, compromised credentials give hackers unfettered access to the target system. Credentials are gained through phishing emails, data leaks from breaches sold on the dark web, and malware.
What’s startling to know is that – 65% of employees use similar credentials across multiple platforms – such practices put your systems at high-level risk especially if these individuals are from your leadership team and IT teams holding administrative access.
Two-factor authentication, password-less authentications, biometrics, and password managers can also help to ensure your organization is equipped to face implicit vulnerabilities of weak credentials.
| FIX: |
|---|
| ➤ Common usernames and passwords lead to most of the hacks. Implementing an effective password policy across the organization can help mitigate this risk ➤ Password sharing across services makes all the applications vulnerable. Avoid using the same passwords across multiple applications and systems ➤ Use two-factor authentication using technologies such as MFA |
2. Malicious Insider
More than 1/3rd of cyber attacks on businesses involve the participation of an internal actor.
These threats take quite a long time to be identified as the attack is coordinated through internal stakeholders who have significant access to company data at the time of the attack.
On average, malicious insider attacks take 231 days to be identified which is 50% longer compared to the time taken in identifying technical misconfigurations.
Disgruntled employees can cause potential damage and enterprises need to be prepared, no amount of reactive management can douse this fire immediately.
Zero trust security limits access privileges of employees to their respective job functions through policy controls and cloud app security features that monitor abnormal data download and sharing behavior among employees.
| FIX: |
|---|
| ➤ Keep an eye on the disgruntled employees by monitoring network and data access for every device to expose the insider risk |
| DEFEAT YOUR CYBERSECURITY BREACH RISK WITH CYSURANCE With enhanced CSaaS Membership, startups get a service guarantee that pays up to $100,000 for breach-related costs. |
3. Misconfiguration
The misconfiguration of cloud services, like Google Cloud Platform, Microsoft Azure, or AWS, or using default settings can lead to data breaches, check your S3 permissions or someone else will.
Misconfiguration happens when there is an error in system configuration.
With the default server configuration not disabled, the hacker can determine hidden flaws, and in turn, fetch additional information. Misconfigured devices and apps present an easy entry point for an attacker to exploit.
Put procedures and systems in place that tighten your configuration process and use automation wherever possible.
| FIX: |
|---|
| ➤ Automate configuration management where possible to prevent configuration drift ➤ Monitor the devices and applications’ settings and compare this with the industry’s best practices. This will reveal any threat for misconfigured devices across your network |
4. Business Email Compromise
As more and more business activity goes online, there is an increased opportunity for cybercriminals to target people in Business Email Compromise (BEC) attacks and other cybercrime.
BEC was responsible for only 4% of the breaches in 2021 but caused the largest financial impact on enterprises.
BEC attacks accounted for around $5.01M average compared to global average cost due to data breach through all attack vectors at $4.24M.
Business Email Compromise (BEC) was also formerly known as Man-in-the-Email scams, where the attackers rely on social engineering tactics to trick unsuspecting employees in the company.
Impersonating C-suite executives through publicly available data on email accounts, the attackers scam their target victims upon careful research and monitoring to transfer hundreds of thousands of dollars.
| FIX: |
|---|
| ➤ Two-factor authentication on all business and personal email accounts ➤ Constant education to employees on various types of spotting phishing schemes employed by hackers ➤ Blocking auto-forwarding of emails |
5. Man-in-the-middle Attack
Man-in-the-middle (MITM) attack is a sophisticated exploit performed to intercept traffic that was supposed to go elsewhere; a hacker achieves this by positioning themself in a conversation between a user and the end application.
This enables the hacker to eavesdrop on the activity between the two parties, intercept data and information while also sending malicious links to unsuspecting parties.
Employees can protect against man-in-the-middle attacks by ensuring they always do business with HTTPS websites, never connecting to public Wi-Fi routers directly, ensuring they have an active internet security solution to guard against MITM attacks deployed through malware, and by making sure home Wi-Fi networks are secure and router firmware is updated periodically.
| FIX: |
|---|
| ➤ Configure devices with certificates and authenticate them with EAP-TLS (Extensible Authentication Protocol-Transport Layer Security) |
6. Phishing
According to a recent IBM global report, phishing attacks are the second most popular attack vector exploited by cybercriminals in 2021.
Phishing attributed 17% of the attacks while incurring an average cost of $4.65M. A phishing attack is a common cyber threat in which hackers target a particular user or group of users with malicious URLs and attachments sent via phishing emails.
When the unsuspecting employees navigate to the malicious URL or attachment in a phishing email, it’ll redirect them to a fake login page tricking them to compromise their credentials.
Hackers use Phishing emails to download dangerous malware such as Adware, Spyware, Trojans, and Ransomware into the enterprise system or networks.
Phishing remains one of the most popular and effective social engineering attack vectors as over 80% of IT professionals today are facing a significant increase in phishing attacks in 2021.
Organizations and employees falling prey to age-old tactics like phishing as an initial attack vector highlights the lack of technology and understanding of phishing attacks among employees.
| FIX: |
|---|
| ➤ Monitor the web-browsing and email click-through behavior of users and their devices to get valuable risk insights ➤ Periodic cyber-security training, zero-trust security models, deploying AI and ML tools for phishing detection can combat such tactics |
7. Third and Fourth Party Vendors
Outsourcing has been rampant since the 1960s, initially ventured as a viable option to run a cost-effective production line. The outsourcing of today has transformed from a value for money alternative to a more skill dependency decision.
Digital Transformation and Industry 4.0 have edged organizations to find the most advanced global partners to deliver bespoke customer experiences.
Per Gartner’s research, 60% of organizations work with more than 1,000 third parties.
The rise in outsourcing poses a vendor-based cybersecurity risk to your customer’s data and your proprietary data. Some of the biggest data breaches were caused by third parties.
| FIX: |
|---|
| ➤ Monitor the cybersecurity posture of the third and fourth-party vendors and fix any vulnerabilities as they appear |
8. Ransomware
Ransomware is a form of cyber-extortion attack seeing record growth in 2021, in the first six months alone over 304.7 million attack attempts were reported by Threatpost.
Cyber-criminals favor ransomware as these attack vectors disrupt the flow of business and damage consumer trust in the organization. Cyber attackers deploying ransomware threats are guaranteed lucrative payouts with minimum efforts once the vulnerability is exploited.
Ransomware makes it to enterprise networks/systems through user-initiated actions such as clicking on malicious links, falling prey to phishing emails or visiting compromised websites.
Once in the network/system ransomware variants encrypt valuable data or block access to the system itself. Once the access to data is denied, ransomware demands a ransom to unblock the files.
WannaCry is one such unpopular ransomware that has infected over 300,000 computers in just 4 days!
| FIX: |
|---|
| ➤ Ensure you have a system in place to protect all your devices from ransomware and keep your Operating System patched and up-to-date ➤ DO NOT install software or give administrative privileges unless you know what it is and what it does |
9. Missing or Poor Encryption
Encryption is a technique used to mask a message by changing its meaning. This protects its digital data by converting it into a code or ciphertext. To read the message, it has to be decrypted first using a decryption key.
Missing, poor, or weak encryption can result in sensitive data such as customer payment information and credentials being exposed to hackers.
Hackers use brute-force attacks to obtain and intercept weak or non-encrypted data. Without strong encryption, organization data can be vulnerable to MITM attacks, when unsuspecting employees connect to public or compromised networks.
Organizations must put preventive measures in place to ensure data is encrypted not just in transit but when at rest and in processing as well.
| FIX: |
|---|
| ➤ Ensure the encryption of sensitive data at rest, in transit, and processing ➤ DO NOT rely on low-level encryption ➤ DO NOT presume that the following compliance means that data is encrypted securely |
10. Distributed Denial of Service (DDoS)
Distributed Denial of Service (DDoS) attacks are deployed by cybercriminals to breach or bypass internet security, the objective through these attacks is to disrupt the normal flow of online business in target companies through unwanted messages, large numbers of traffic, and requests from different sources.
The increased computation required to be performed to address a large number of process requests will eventually cause disruption of services or even crash of the services.
A potential mitigation method for DDoS is to use CDNs, reverse proxies, HA proxies that put layers of defense in between systems serving content and clients requesting content.
| FIX: |
|---|
| ➤ Ensure a high level of network security ➤ Enable server redundancy to mitigate the risk ➤ Look out for warning signs such as poor connectivity, slow performance, crashes, unusual traffic from a set of IPs, high demand for a single page or endpoint, etc |
BONUS
Finally, we have the – Brute Force, while we uncovered the top 10 common actor vectors to guard against in 2022, Brute Force can deserve a special mention.
With Brute Force, the hacker works across all attack vectors described above; including password attacks, breaking weak encryption, etc, so it is not technically an attack vector on its own.
Cyber-criminals use this type of attack which is based on trial and error to tenaciously gain access to an organization until one attack works.
Cyvatar’s Managed Cyber Threat Prevention
Cyber Threats are everywhere, and they are only getting more formidable with the rise in utilization of AI & ML techniques, remote working of employees, and lack of updated cybersecurity personnel in most organizations.
At CYVATAR.ai, our goal is to extend a new age of cybersecurity solutions to our partners to ensure they continue doing what they do best – handling their businesses, while we deliver security expertise, proven solutions, and services to prevent any attack vectors coming your organization’s way! Get started now for free to transform your business cyber-secure in 2022!
| DEFEAT YOUR CYBERSECURITY BREACH RISK WITH CYSURANCE With enhanced CSaaS Membership, startups get a service guarantee that pays up to $100,000 for breach-related costs. |