What is Vulnerability Management and why is it important for SMBs?

What is Vulnerability Management and why is it important for SMBs?
Aileen Casmano | 02/17/2022What is Vulnerability Management?
Cybercriminals are a relentless lot. They are always on the lookout for any new vulnerabilities in an enterprise’s cyber defense system.
So, it’s important that defenders keep a constant eye on emerging threats and any vulnerabilities that may exist in their organization’s IT infrastructure and remedy them in time to avoid the attackers exploiting it.
A vulnerability can be any weakness or weaknesses that may exist in an enterprise’s network, operating systems, application tools, and end-user applications that are susceptible to be exploited by cybercriminals to run malicious code, malware, or steal sensitive data.
And no, vulnerability is not the same as risk and threat. There are many differences between vulnerabilities, threats, and risks.
Vulnerabilities could be due to:
- Hardware: Climatic conditions like dust, extreme heat, extreme humidity can lower the hardware’s capabilities, cause damage to motherboard, CPU, etc.
- Software: Vulnerabilities due to outdated software or flawed design, poor testing, violations of memory safety, input validation errors, privilege execution bugs, directory traversal, email injection, etc.
- Network: Poor configuration, unsecure architecture and communication lines, poor authentication.
- Organization: Poor cyber hygiene, lack of awareness and training, poor audit, lack of security plan, lack of incident response plans, etc.
Vulnerabilities are ever-changing. Even as the present vulnerabilities are fixed, newer ones emerge. So it’s important to keep a tab on the emerging vulnerabilities.
At any given point in time, an enterprise may be having several hundred to thousands of vulnerabilities. But all of them do not expose the enterprise to the same kind of risk.
Some may be high risk and need to be fixed on a priority basis, while others may be low risk and do not require immediate attention.
To safeguard their enterprise, cyber defenders in an organization need to identify, analyze, remediate and report vulnerabilities on a continuous basis.
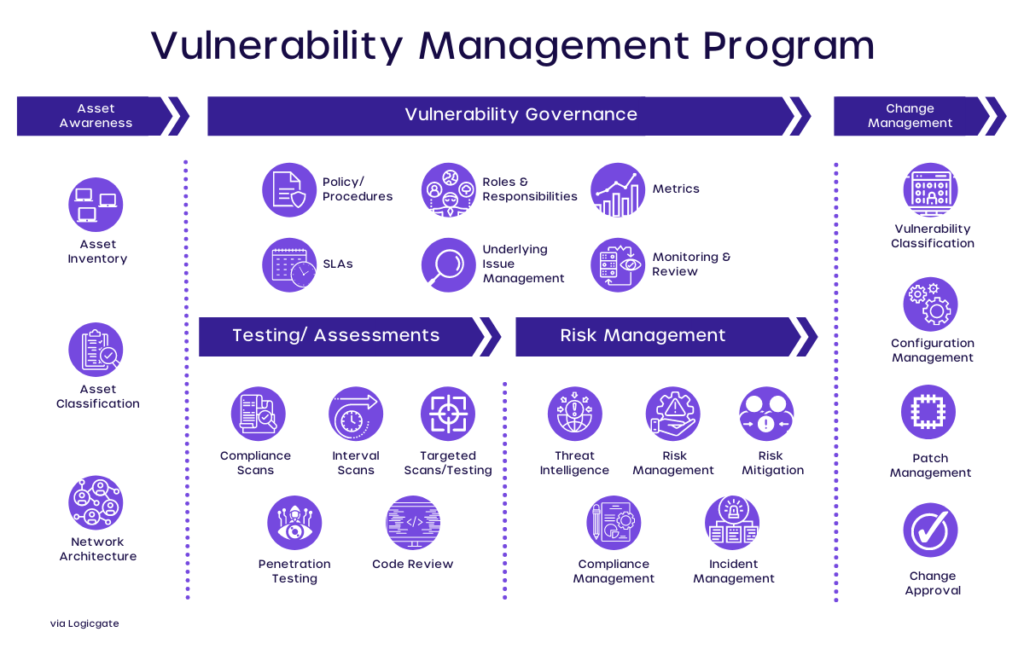
The organized practice of proactively identifying, analyzing, and remediating vulnerabilities is known as Vulnerability Management and is an essential part of an enterprise’s strong cybersecurity posture.
How do you rank and categorize vulnerabilities?
The common vulnerability scoring system (CVSS) is an open industry standard to assess the severity of vulnerabilities in a system. The CVSS score ranges from 0.0 to 10.0.
The National Vulnerability Database (NVD) adds severity ratings for the respective CVSS scores.
| CVSS Score | Severity Rating |
|---|---|
| 0.0 | None |
| 0.1 – 3.9 | Low |
| 4.0 – 6.9 | Medium |
| 7.0 – 8.9 | High |
| 9.0 – 10.0 | Critical |
Why Do We Need Vulnerability Management?
As we have already noted, vulnerabilities keep growing. The National Vulnerability Database lists some 2384 vulnerabilities for December 2021 alone.
Remote Working and new technologies like cloud-based services, IoT, SaaS, etc have only increased the vulnerabilities further.
So, finding and fixing vulnerabilities on a continuous basis requires a concerted, disciplined effort. Vulnerability Management helps enterprises perform this vital task.
Vulnerability Management helps you avoid cyber attacks, data leaks, and losses before they happen.
“Nearly 60% of the cybersecurity breaches that occurred in 2019 were completely avoidable because they were due to known vulnerabilities and could have been patched easily.”
Ponemon Institute Report
Vulnerability Management provides you with the right tools and processes to continuously identify and remedy high-risk vulnerabilities.
One needs it for achieving compliance with Industry Standards and Regulations like ISO 27001, HIPAA, GDPR, etc.
Vulnerability Management Process
Generally, the Vulnerability Management process consists of 4 steps:
- Identification of vulnerabilities
- Evaluation of vulnerabilities
- Remediation of vulnerabilities
- Reporting vulnerabilities
1. Identification of Vulnerabilities
This is the initial step. Here you attempt to identify existing vulnerabilities throughout the enterprise’s IT infrastructure.
To do so, you must first make an inventory of all your IT assets and choose the right kind of Vulnerability scanner for each kind of asset.
The scanning consists of 4 stages:
- Ping and scan network-accessible systems
- Identify open ports and services running on the systems
- Remotely log in to the system and gather detailed system information
- Correlate the gathered information with the existing vulnerabilities
Vulnerability scanners are essential tools in identifying vulnerabilities. They are used to identify different systems running on a network, like desktops and laptops, physical and virtual servers, firewalls, databases, printers, etc.
The identified systems are then tested against different attributes like operating system, installed software, system configurations, open ports, and the like.
This information is then used to associate known vulnerabilities contained in a vulnerability database like the NIST Vulnerability database that is publicly available.
You will need different kinds of scanners to identify vulnerabilities in your network and the applications you use.
Per the Center for Internet Security, enterprises should carry out at least one vulnerability scan per week to secure their IT assets. More frequent scans will only enhance your security.
2. Evaluation of Vulnerabilities
Once the vulnerabilities have been identified, the next step is to evaluate them for the severity of the risk they pose and be dealt with. Vulnerability Assessment is a critical part of it.
One way to do this is to use the Common Vulnerability Scoring System to know the severity and magnitude of the risks, which risks should an enterprise focus on, etc.
Along with these scores, enterprises should consider additional factors like:
- Is there a publicly available exploit code for this vulnerability?
- How difficult or easy is it to exploit this vulnerability?
- Does this vulnerability directly impact the security of your product?
- If exploited, what would be its impact on your business?
- How old is the vulnerability and how long has it been there on the network?
- Are there any security controls in place to reduce the likelihood and the impact of this vulnerability?
- Is this vulnerability true or false positive?
Vulnerability scanners can sometimes come up with false positives. You need to perform penetration testing to validate whether the detection is true or false positive.
If it turns out to be a false positive, the enterprise can then focus on the real, high-risk vulnerabilities.
3. Remediating Vulnerabilities
Once the vulnerabilities are validated and are known to pose a risk, the next step is to prioritize them and deal with those vulnerabilities.
There are three ways of remediating the identified vulnerabilities:
- Remediation: Completely preventing exploitation by correcting, or replacing the code that contains the vulnerability or patching the system on the whole. This is the most ideal strategy to adopt.
Patch management is one of the means through which the vulnerable parts of an asset receive security patches.
- Mitigation: Reducing the impact of a vulnerability. This is a temporary solution until one takes care of the vulnerability completely. This is sometimes necessary when an appropriate fix or a patch is not available immediately.
- Acceptance: Taking no action against the vulnerability. This is done when the vulnerability poses a low risk or no risk and the cost of fixing it costs more than if it is exploited.
The right remediation approach needs to be determined by the enterprise’s security team, system owners, and administrators.
When the remediation process is complete, it is useful to run a vulnerability scan to ascertain that the vulnerability has been completely eliminated.
4. Reporting Vulnerabilities
Performing regular vulnerability assessments helps enterprises understand how good and effective their Vulnerability Management program is.
It helps them to adopt the most cost-effective remediation techniques to address most vulnerabilities.
Consistent reporting helps enterprises with most of their compliance and regulatory requirements.
As noted in the very beginning, threats and attacks and vulnerabilities are always evolving and enterprises need to keep pace with them.
Every time a new device, network, or application is added to the IT infrastructure or a new partner, employee, client, or customer is added to the enterprise network, it only exposes the enterprise to further vulnerabilities.
Constant vulnerability assessment and reporting helps in understanding the vulnerabilities and the risks they pose and hence, taking suitable remedial action.
One can do vulnerability management in-house or enterprises can avail of the security services of a Managed Security Services Provider like Cyvatar.
Vulnerability Management Metrics
It is not enough that enterprises put in place a comprehensive vulnerability Management process.
They need to ensure that the detection and remediation tools are producing comprehensive, up-to-date reports.
Vulnerability Management Metrics provides the best information about how good is your Management plan, how well it is performing, whether there is room for improvement, etc.
Vulnerability Management Plan
In order to build a sound vulnerability management program, one requires a clear vulnerability management plan.
Enterprises should prepare a vulnerability management policy that keeps pace with the constantly evolving challenges of cybersecurity and the complex technology and business ecosystem.
Vulnerability Management policy must not only include all the 4 stages of the vulnerability management process but also include continuous scanning across all parts of the software development cycle with both application security testing tools and protection tools.
It must also cover an enterprise’s network infrastructure, servers, operating system, virtual machines, services hosted on the cloud, databases, proprietary, third-party, and open-source applications, and devices owned by the enterprise.
The policy must clearly state what it is monitoring and how it is monitoring.
Each of these devices and environments presents a different set of vulnerabilities and risks.
So, it’s important that a good vulnerability management policy addresses each type of vulnerability and risk and ensures that the right tools and processes are in place to deal with them.
Finally, the policy must emphasize prioritization. Although the goal of Vulnerability Management is to fix all kinds of vulnerabilities, it is impossible to do so.
Hence focusing on the high-risk vulnerabilities is important.
Challenges Of Implementing A Vulnerability Management Program
Crucial as it is for every type of organization – be it large organizations, small and medium-sized businesses, or startups- to put in place an effective vulnerability management program, many find it very challenging to do so.
The major challenges facing them are:
- Resource crunch: Tight budgets, lack of expertise, and human resources.
- Wrong prioritization: As technology evolves and activities in cyberspace expand, vulnerabilities also keep growing.
This poses a huge challenge to security teams as they can’t fix everything. So, they prioritize the highest risks. But sometimes, this can be tricky and lead them the wrong way.
- Poor communication: Good and effective communication between the security team, the board, and employees of an enterprise regarding vulnerabilities and their remediation is critical.
But often poor communication hampers the proper implementation of vulnerability management programs.
- Lack of continuity: A vulnerability Management program needs to be continuous and ongoing. Many enterprises find it very challenging to implement such a program due to various constraints- be it cybersecurity budgets or the right expertise.
Vulnerability Management Tracking Tool by Cyvatar
Vulnerability Management processes need to be continuous. But, many well-funded startups, SMBs, and small enterprises find this very challenging due to lack of cost-effectiveness and limited supply of highly qualified cybersecurity professionals. Companies, usually, lack the staff with the necessary expertise and experience, and exposure to handle the subtleties and nuances of implementing the Vulnerability Management program.
Cyvatar’s Threat & Vulnerability Management is a potent way to manage vulnerabilities– that’s extremely cost-effective and comes with deep expertise to install guardrails to safeguard your businesses from online threats.
Cyvatar brings together the people, technology, and processes that offer comprehensive security to your organization.
Talk to our experts today to understand the options that your organization has to deter threats and fix vulnerabilities.