Metaverse A-Z: What is it and what’s the hype all about it?

Metaverse A-Z: What is it and what’s the hype all about it?
Cyvatar | 05/02/2022Metaverse is more than just some virtual reality. It holds the key to the future of the internet. It will change the way we interact online. However, there’s a catch. Read on..
The metaverse explained
The simple definition of the Metaverse is that it is the next iteration or avatar of the internet. Do not think of the Metaverse as a replacement for the internet, more of it is a concept that hopes to build on the foundations of the internet.
In the Metaverse, users travel to a virtual world that simulates the physical world through technologies such as Virtual Reality (VR), Augmented Reality (AR), digital currency, social media platforms, and blockchain.
With the integrated use of these technologies, the Metaverse aims to provide a rich user experience equivalent to the real world.
Is the Metaverse a new concept?
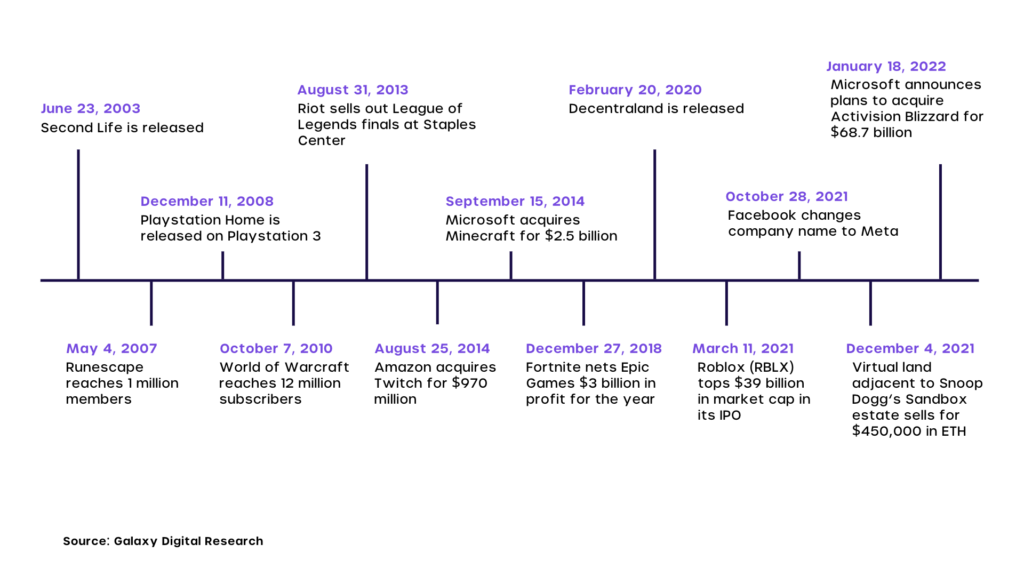
No, the term metaverse has been prevalent for quite some time. It was first described in the novel Snow Crash by author Neal Stephenson, published in 1992. Several companies later created virtual communities based on the idea, the most famous example of which was Second Life, which made its debut in 2003.
People in the metaverse use avatars to represent themselves, communicate with one another, and virtually build a community.
In the Metaverse, digital currency is used to purchase clothing, weapons, shields in video games, and various other items.
Users can also use a virtual reality headset and controllers to travel through the Metaverse for fun with no specific goal in mind.
The current iteration of the Metaverse follows closely in line with a genre of video gaming known as MMORPG (Massively Multiplayer Online Role-Playing Game).
MMORPGs follow a similar concept to the Metaverse, where gamers or users can interact and play in a simulated digital world, trade in in-game economies, complete quests and objectives to progress in the game.
One could say this is the Metaverse with the gamification aspects removed.
An example of MMORPGs is the widely popular World of Warcraft, a game that has garnered millions of online users for over 20 years.
The Metaverse has run the rounds in mainstream media and in recent history. The movie Ready Player One explored the Metaverse concept, where gamers would be transported to a virtual world and interact with each other through customized avatars.
Multiplayer video game Fortnite also explored an aspect of the Metaverse by organizing the first digital music concert where millions of players were in attendance.
What will the metaverse look like?
A question that often ponders users of the internet and social media is: “What will the metaverse look like?”
Will the metaverse look like the dystopian future depicted in the novel Snow Crash, where it was first coined and mentioned?
Will the metaverse look like a simulated video game like the Sims or Second World?
The answer is still a mystery, but with virtual headsets and the eventual acceptance of cryptocurrencies, digital assets, and NFTs, the metaverse will look a lot like a world within a world, a simulation of sorts where you can interact with other people, all at the click of a button.
Current metaverse companies
Even though Facebook owner Mark Zuckerberg was the one to announce the imminent arrival of the Metaverse by rebranding his company Facebook to Meta, many other companies are placing their hats in the ring for the metaverse concept.
Here are some of the companies with significant investments in the building of the Metaverse:
1. Epic Games
Epic Games, owners of the massively popular video game Fortnite (350+ Million Users Worldwide) and creators of the Unreal Engine, which is popular among developers, have staked their claim on building the Metaverse after securing a $1 billion round of funding in 2021.
This round of funding also featured investment from Sony, which funded around $200 million to develop Epic’s version of the Metaverse.
It’s believed that Epic’s approach to the Metaverse would be different from Facebook’s, with the aim of providing a safe communal space for users without being filled with ads and marketing.
Epic has previously experimented with concepts derived from the Metaverse, such as hosting large-scale digital concerts featuring artists Ariana Grande and Travis Scott.
They also made an immersive reimagining of Martin Luther King’s iconic speech ‘I have a Dream’ with photo realistic aspects.
Epic also has a tie-up with luxury brand Balenciaga, with a deal that will eventually have real-world fashion designs available virtually for digital avatars.
2. Microsoft
Microsoft is already known to utilize holograms and is working on mixed and Extended Reality (XR) applications that combine the real world with augmented reality and virtual reality through its Microsoft Mesh platform.
It revealed in 2021 its plans to bring mixed-reality, including holograms and virtual avatars in 2022. This feature will be known as Microsoft Mesh.
According to Microsoft, Mesh will allow users to establish a virtual presence on any device by using a customized avatar of themselves.
This follows the earlier announcement of Mesh for Microsoft, a developer platform that includes a suite of AI-powered tools for avatars, session management, spatial rendering, multi-user synchronization, and “holoportation.”
Holoportation is a real-time 3D capture technology that allows users to reconstruct and transmit high-quality 3D models of people.
Microsoft has already collaborated with Accenture’s professional services firm to develop Mesh-enabled immersive environments.
Accenture hires over 100,000 people each year and uses Mesh to assist with onboarding new employees.
Explorable 3D virtual connected spaces for retail and workplaces are also in the works for next year.
Also, the United States Army is collaborating with Microsoft on an augmented reality Hololens 2 headset for soldiers to train, practice, and fight in.
Thanks to their video game console, the Xbox, and their online game service: Xbox Live, Microsoft is already connected to millions of video game players worldwide.
3. Roblox
Roblox, the virtual game platform created in 2004, houses a number of user-generated games, including role-playing offerings like Bloxburg and Brookhaven, where users can build homes, work, and play out scenarios.
After going public this year, Roblox is now worth more than $45 billion.
Since then, Roblox has partnered with skateboarding shoe company Vans to establish Vans World, a virtual skateboarding park where players can accessorize in fresh Vans gear, and opened a limited Gucci Garden, in which you can try on and buy clothing and accessories for your virtual personality.
4. Meta
Formerly known as Facebook, Meta has made large investments and taken steps towards its version of the Metaverse.
With the procurement of Oculus, a virtual reality headset company, Meta aims to build a world based on virtual reality, that allows digital avatars of users to interact with each other for work, entertainment, and even travel all through the use of VR headsets.
Facebook founder Mark Zuckerberg is fully confident that the Metaverse will soon replace what we know currently as the internet and hopes to build something so immersive that users are part of the experience instead of just being observers.
After the news about Meta broke out, the company also released ‘Horizon Worlds’. It is a VR space that a user can explore and navigate with an avatar and provides developer tools to create more worlds in the future.
What is the purpose of the metaverse?
Today, people use the Internet to communicate information in a variety of ways, including email, chat rooms, blogs, social networking, and so on.
The Internet’s dilemma is that it is a two-dimensional world. While it allows you to interact with other people and objects, it has several limitations. As a result, the Metaverse was born.
The Metaverse is a three-dimensional environment in which you may interact with other people and items in a more natural way.
The Internet, on the other hand, is constrained by the fact that the individuals you connect with are merely pixels on a screen.
The Metaverse allows you to see, hear, and interact with your surroundings outside of the constraints of your screen.
NFTs and the metaverse
What are NFTs?
Non-fungible tokens (NFTs) are blockchain-based cryptographic assets with unique identifier codes and metadata that differentiate them from one another.
They cannot be marketed or exchanged at equivalency, unlike cryptocurrencies. This is in contrast to fungible tokens, such as cryptocurrencies, which are identical to one another and can thus be used as a medium for commercial transactions.
How do NFTs work?
NFTs are essentially digital versions of tangible collector’s artifacts. As a result, rather than receiving an actual oil painting to put on the wall, the customer receives a digital file.
They also obtain exclusive rights to the property. It’s true: NFTs can only have one owner at a time. Because NFTs include unique data, it’s simple to verify ownership and transfer tokens between owners.
They can also be used to hold specific information by the owner or author. Artists, for example, can sign their work by putting their signature in the metadata of an NFT.
The Ethereum blockchain contains the majority of NFTs. Ethereum, like Bitcoin or Dogecoin, is a cryptocurrency, but its blockchain also supports these NFTs, which store extra information that allows them to function differently.
An NFT is made up of digital objects that represent both tangible and intangible objects, such as:
- Collectibles
- GIFs
- Art
- Designer sneakers
- Music
- Virtual avatars
- Video game skins
- Sports and video highlights
Don’t forget the tweets. Even they form part of NFTs. Thanks to Jack’s first-ever tweet.
When bidding on the “Valuables” platform, which is administered by Cent – a blockchain-powered social media network, Jack Dorsey sold his first tweet as an NFT, or non-fungible token, for nearly $2.9 million. The Twitter user @sinaEstavi bought it.
How do they work in the metaverse?
Non-fungible tokens (NFTs) are expected to play a significant part in the Metaverse’s utility and popularity. NFTs are a sort of secure digital asset that uses the same blockchain technology as cryptocurrency.
An NFT can represent a work of art, a piece of music, or digital real estate instead of currency. An NFT provides the owner with a digital deed or proof of ownership that may be purchased or sold in the Metaverse.
For example, Metaverse Properties claims to be the first-ever real estate company that will deal with properties in virtual reality.
The company will aim to work as a broker or agent for real estate properties in many metaverse worlds like Decentraland, Sandbox, Somnium, and Upland to name a few.
That’s not the only company to do so, however. Nike recently acquired the company RTFKT, which mainly creates virtual one of a kind sneakers and digital artifacts. One can acquire them via NFTs.
Nike even tied up with platform ROBLOX to create a virtual world called Nikeland where players can interact, play and dress up their virtual avatars with digital Nike Gear.
Crypto and the metaverse
Now that we’ve established the purpose of NFTs in the metaverse, let’s talk about what could be the currency of the metaverse.
In the imminent future, we will need methods to procure virtual items, which requires a secure way to show ownership.
We will also need to feel secure when transferring money and virtual tokens; this is where cryptocurrencies come in. While the metaverse is still nascent, expect developers to focus on implementing blockchain technology.
The main benefit of implementing blockchain into the metaverse is its decentralized transparency in terms of dealing with currency and finance.
You could even say that blockchain emulates how currency works in video games. This holds true as gamification is quite common when it comes to decentralized finance (DeFi)
And GameFi.
There will be so many similarities that the virtual and real-world will only get more and more integrated in time.
In terms of key aspects, here is how blockchain works with the metaverse:
1. Proof of Digital Ownership
An online wallet is one of the most secure and reliable ways to establish a digital identity and proof of ownership. You can instantly prove ownership of an activity or an asset on the blockchain if you own a wallet with access to your private data.
To prove accountability, you could show an exact transcript of your transactions on the blockchain while at work.
2. Digital Collection
Just as users can determine who owns something, we can also demonstrate that it is original and one-of-a-kind. This is paramount for a metaverse that wants to incorporate more real-life activities into it.
We can use NFTs to create completely unique objects that one can’t replicate or forge. A blockchain can also represent physical item ownership.
3. Reliable Transfer Tools
The metaverse will require a secure method of transferring value that users can rely on. If users spend a significant amount of time in the metaverse and even earn money there, they will require a trustworthy currency.
In-game currencies in multiplayer games are less secure than blockchain-based crypto.
4. Blockchain is Governable
Users should value the ability to control the rules of their interactions with the metaverse. In real life, we have the ability to vote for corporations and elect leaders and governments.
The metaverse will also require methods for implementing fair governance, and blockchain is already a proven method for doing so.
5. Ease of Access
On public blockchains, anyone from anywhere in the world can create a wallet. Unlike a bank account, you don’t have to pay any money or provide any information.
As a result, it is one of the most accessible methods of managing finances and online digital identity.
6. Interoperability
The compatibility of different platforms is constantly improving thanks to blockchain technology. Polkadot (DOT) and Avalanche (AVAX) projects enable the creation of custom blockchains that can engage with one another.
A single metaverse will connect various projects, and blockchain technology has already provided solutions for this.
When will the metaverse come out?
Facebook founder Mark Zuckerberg, soon after revealing the rebranding of Facebook to Meta, explained that the Metaverse is imminent but at least 10 years away from being fully realized.
One setback to the rise of the Metaverse was explained by Microsoft owner Bill Gates, who says that the reason the Metaverse isn’t here yet is that VR goggles are quite expensive to produce and sell and that many consumers do not have access to Virtual Reality (VR) yet.
There have been advancements, however, with Meta trying to produce more economical VR headsets like the Quest 2 and the up-and-coming virtual platform Horizon Workrooms.
Horizon Workrooms aims to replace physical offices with virtual offices where employees can gather with virtual avatars and work/ interact with each other.
It aims to improve on Google Meet and Zoom work calls, which saw a surge in use, during the COVID-19 pandemic.
The other drawback currently is the level of technology required to efficiently run a metaverse world.
Current technology still needs to improve in terms of motion capture gloves, recognition of body language of the user, and proper voice recognition to work in tandem with each other for a successful and smooth experience.
Metaverse Expectation vs Reality
When it comes to user beliefs, the Metaverse expectation is a virtual world that is at least a few decades away. But that isn’t completely true, because our current reality is halfway to the metaverse expectation with the invention of VR headsets, virtual classrooms, and offices.
As technology gets more advanced and affordable, the full metaverse expectations and experiences presented over the decades in books, movies, and popular culture will become closer to reality.
If the metaverse has to be a reality and be widespread, one needs to take care of the following area, in particular:
- Technology
- Commercial infrastructure
- Privacy and identity
- Workforce of the future
- Regulation, tax, accounting, and social infrastructure
Cybersecurity challenges in the metaverse
The Metaverse will come with its own set of challenges.
Consider talking to your supervisor about a top-secret multimillion-dollar agreement. The conversation comes to a close, and you both go.
You both meet up again a time later, and you bring up your previous talk. However, your boss has no recollection of it.
What just happened here?
You were just the victim of a deep fake or hacked avatar in the metaverse.
The following cybersecurity challenges are obvious in the metaverse:
- Identity security
Imagine 10 years from now, we are in a virtual metaverse meeting. Each person has their own avatar in the virtual world. However, how can we be sure that we are interacting with the right person?
For harmful purposes, an attacker could mimic a legitimate participant. Consider what would happen if a competitor’s spy was present at a regular business meeting. What if the the imposter replaced the boss?
Anyone who can obtain credentials or gain access to a metaverse account in any other way effectively becomes that person. Identity theft, eavesdropping, and social engineering have never been easier. - Data breaches
As users leave data trails across the metaverse, a major concern in the real world — the invasion of user privacy by internet businesses — may make its way into virtual reality.
Within seconds, one identifies that it is you, and it’s a serious potential privacy concern for the virtual world.
The only way to solve this is by fixing the weakest link in cybersecurity. Organizations need to train their staff against common cyber threats.