What helps protect your business from spear phishing? Top techniques

What helps protect your business from spear phishing? Top techniques
Cyvatar | 04/25/2022Email is the gateway if you want to get inside a company. Since it offers the door to an organization, spear phishing is one of the most powerful arsenals in the hands of cyberterrorists who want to wreak financial and reputational havoc.
The only thing that stands between a spear-phishing attack and a potential breach is how the email recipient responds to it.
If the email recipient doesn’t spot the spear-phishing email and ends up engaging with it, then it opens a Pandora’s box that requires immediate remediation steps.
Cybercriminals are adept at manipulating people. In this article, we are going to look at spear-phishing and what helps protect businesses from spear phishing.
Cyble says that a successful spear-phishing attack can cost $1.6 million on average. If you are confident that you can protect your organization against spear-phishing attacks, then you need to think again.
What is spear phishing in Cybersecurity?
It is a phishing method that targets specific individuals or groups within an organization. While the main objective is to steal data for malicious purposes, cybercriminals are also known to install malware on the victim’s computer.
Here’s a rundown of how it works: You get an email from a source you trust. Unfortunately, clicking on it leads you to a vortex of malware. They use clever strategies to get the victims’ attention.
How does spear phishing work?
The main reason behind spear phishing’s high success rate is authenticity. It is as unfortunate as it sounds.
Cybercriminals collect legitimate information about the victims through several sources: social networking sites, forums, and by collecting details. Using all the information, they create a personalized message that will draw in the victims.
The criminals send a highly enticing email and ask the victim to directly respond to their email. The message could include a malicious link or have an attachment that installs malware on the device.
When they click on the link or the attachment, the victim is tricked into sharing private and confidential information such as user credentials or financial information.
Top spear-phishing techniques
Being aware of the different types of spear-phishing attacks is important because it makes recipients more wary.
Below are the three common spear-phishing techniques employed by cyber attackers:
- Business Email Compromise (BEC): BEC attacks involve hackers accessing or spoofing emails of a senior executive to ask for documents, login information, or money.
Senior staff members, attorneys, trusted vendors, and partners are usually targeted in this. A successful BEC attack can result in the compromise of business systems, unlawful entry into the victim’s credentials, and massive financial losses. - Whaling: Only C-suite executives and similar high-profile targets are attacked here. Just like BEC attacks, whaling attacks are also customized for the recipient.
It uses the same social engineering and spoofing methods to steal sensitive information. - Clone Phishing: In this type of attack, hackers create replicas of legitimate messages to trick the victim into believing that the message is real. Even though the message will look valid, the attachment or link will be malicious.
Clone phishing attacks involve cloned websites that have a spoofed domain that mimics a legitimate one.
Examples of infamous spear-phishing attacks
- Elara Caring, a US-based healthcare service provider, had to face a spear-phishing attack that targeted two employees.
They gained access to the employees’ email accounts, birthdates, financial and insurance information, social security numbers, and driver’s license numbers of more than 100,000 elderly patients. - Ubiquiti Networks suffered a $46.7 million loss due to spear-phishing attacks. The company said that the fraud involved “employee impersonation and fraudulent requests from an outside entity targeting the company’s finance department.”
- As ironic as it may sound, Epsilon, the world’s largest email service provider, was spear-phished in 2010.
Despite warnings from Return Path, one of its business partners, about attackers targeting email service providers, Epsilon did not take immediate action. The attackers stole data from at least 50 companies, including Best Buy, Citi, Hilton, Marriott, and Target. - Hackers didn’t spare the United States’ presidential elections either. In 2016, hackers created a fake email using Gmail and requested users to change their passwords because of suspicious activity.
Using this, they gained access to hundreds of emails that offered them information about the Democratic Party’s campaign. - Employees at Sony were lured by fake Apple emails that led to thousands of files, including financial documents, employees’ information, and business agreements, being stolen.
Investigations revealed that the cyberattack was orchestrated by the North Korean government.
- 100 million emails of Amazon customers were compromised when they opened an email titled “Your Amazon.com order has dispatched.” Locky ransomware ransomware was attached to the email. The ransom was paid in bitcoins.
- German-based manufacturing giant Leoni AG lost $45 million after its finance department was tricked into transferring funds to the wrong account.
- In 2019, Toyota Boshoku Corporation, a major Toyota auto parts supplier, was the victim of a BEC attack where they persuaded a finance executive to change the recipient’s bank account information in a wire transfer. They lost $37 million.
- It was through a spear-phishing email that cyberterrorists were able to get into one of the world’s largest retail stores, Target.
They gained access to the credit card and debit card information of more than 40 million customers. The criminals had installed malware on Target’s partner company.
How do you identify a spear-phishing attack?
According to Proofpoint, in 2021, 83% of businesses will have had a successful email-based phishing attack where they tricked people into clicking on a bad link, downloading malicious software, giving out their passwords, or making a wire transfer.
This makes it all the more important to identify a spear-phishing email when you see one.
Below are some of the characteristics common to spear-phishing emails:
1. Even though the sender’s email address looks as if it is from a trusted source, closer observation will lead you to simple grammatical or typographical errors. You might find an alphanumeric character for another one that has a close resemblance to.
2. Further looking into the email’s source, you can look for SPF and DKIM records. If they pass, that shows it comes from the intended recipient.
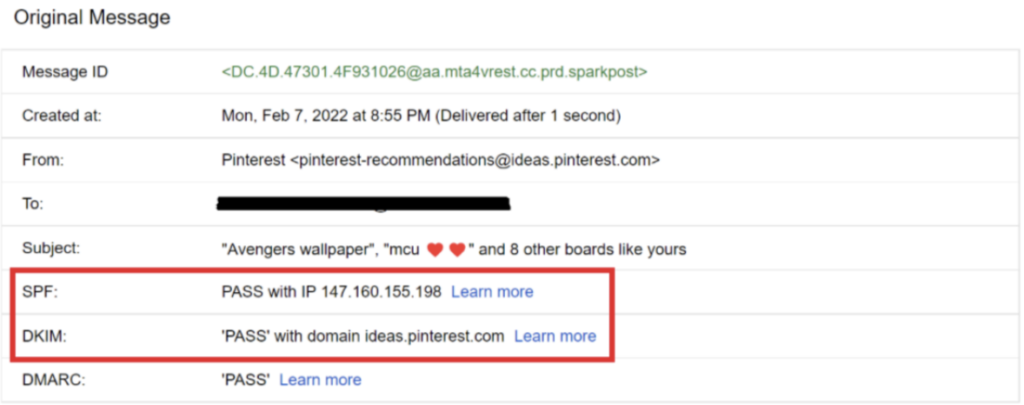
3. Spear phishing emails evoke a sense of urgency. They mark it as urgent, especially when the task they persuade you to perform is against the company’s policies.
4. The language that you see in the body of the email will not look professional. A seasoned professional can easily figure it out.
5. The jargon used in the email will be incorrect.
6. The tone of the message will be completely different from how the user usually communicates.
Top techniques to protect your business from spear phishing
The highly targeted nature of spear phishing makes it difficult to detect them. Even a well-trained observer can be distracted and commit errors.
It is critical to include user training with technical solutions so that you end up preventing spear-phishing emails in your company’s inboxes.
Thankfully, there are several spear phishing solutions to protect your business from it.
- Maintain system updates
Keep checking for the latest security updates for your OS. No matter which OS you run, Windows, Apple, Linux, or AIX, all of these have security patches.
They keep releasing new ones to predict new phishing attacks. Ensure that you keep your internal and customer-facing systems up to date.
- Encrypt sensitive information
Protecting sensitive information from the wrong hands starts with file encryption. The files you send to your systems, cloud environments, remote locations, etc., should be decrypted so that it will not matter even if they go to the wrong hands.
Here are a few things in your organization that you should encrypt:
- Passwords
- Security questions
- Internet usage (VPN and masked IP address)
- External storage in the form of USBs, external hard drives, etc.
- Cloud storage
- Hard drives
- Business agreements, audit reports, tax documents, etc.
It’s best to use a service that manages file transfers because they encrypt your files with safe encryption methods.
They also ensure that you stay updated with the encryption standards, which keep changing over time, thereby making your data transfers safer.
- Password management policies
Employees can’t use corporate access passwords on fake websites if they have a fool-proof password management system in place.
You can tell your employees to provide a false password when they are accessing a link that came in an email.
Phishing websites will accept fake passwords, but a legitimate website will never do that. It will help them identify phishing sites using this method.
- Leverage analytics
Use a detailed analytics tool that will assess the company’s inbound email history for the past year. Analytics software will go through the email content, identify suspicious emails, and assess the user’s behavior with these emails. A deeper look at historical email data will help towards improving security.
- Security awareness training
You can reduce the likelihood of employees falling for spear-phishing emails by training them to handle emails carefully.
Strategies on how to recognize phishing emails should be part of the training. They should learn how to look for suspicious domains, links in phishing emails, words in the message, and how to report them when they get such phishing emails.
The employees should be taught what they should do if they come across a spear-phishing email. You can even purchase training materials from vendors or outsource this task.
- Conduct external audits
Most audit firms these days offer social engineering audits that measure how internal employees behave with critical IT assets.
Since spear phishing is a serious phenomenon, it makes sense to allocate a certain budget for a social engineering audit throughout the organization.
Outside audits will not be biased, and they will have a genuine intent to find any issues in the infrastructure or suspicious employee behavior so that any vulnerabilities can be removed.
- Leverage AI
There are machine learning tools that analyze the structured communication patterns in an organization. It will be able to spot anomalies that have the signs of a potential spear-phishing attack.
You can find solutions that detect and block spear phishing attacks, including Business Email Compromise (BEC) and brand impersonation.
- Use DMARC technology
Even the safest-looking email might not actually be one. Unfortunately, cybercriminals can also spoof the email sender’s address and send emails posing as a company representative. The success rate of phishing emails is high because of how genuine those emails look.
The DMARC (Domain-based Message Authentication, Reporting & Conformance) technology employs the Sender Policy Framework (SPF) and Domain Keys Identified Mail (DKIM) to analyze the emails against your existing database.
When the email doesn’t match the record for the sender, the DMARC rejects it and sends a report to the security admin.
DMARC is the only email authentication protocol that ensures spoofed emails do not reach inboxes.
Some of the top companies like Google, Yahoo, Microsoft, and AOL use DMARC to stop spear phishing. Here’s a disclaimer, DMARC shouldn’t be the ‘only’ tool to protect yourself against spear phishing.
- Implement multi-factor authentication (MFA)
Businesses across the globe have warmed up to using MFA for user authentication. Google even recommends turning on MFA if you want to secure it even more.
MFA requires more than one piece of authentication. The extra authentication could be a password and a number generated randomly on a login token.
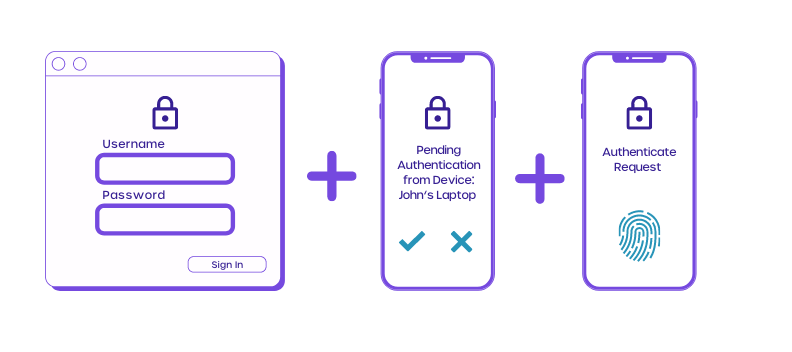
Doing this makes it incredibly difficult for hackers to gain access to your systems.
Conclusion
Cybercriminals usually get their way because they are extremely sophisticated at manipulating people.
The only way to stay one step ahead of them is by being mindful of the emails that you open and the resources that you use to protect yourself. By following the strategies that we have mentioned in this article, you can keep your organization and customers safe.
Spear phishing protection is something that businesses should give a lot of attention to and put a lot of effort into.
| Worried about the Spear-phishing attacks? Talk to our cybersecurity experts. |