How blockchain will revolutionize and elevate the banking sector

How blockchain will revolutionize and elevate the banking sector
Cyvatar | 03/28/2022Blockchain’s tamper-proof distributed ledger technology makes it a must-have for the banking sector.
Even though blockchain came into existence in 2008, we can safely say that we are seeing only a fraction of the use cases possible as it is still considered to be in its ‘infancy.’
Think of blockchain as an online version of one of those big leather-bound ledgers which businesses use for recording transactions. That’s the blockchain for you, and it has provided a positive jolt to the banking industry.
| SAY NO TO CYBERSECURITY JOLTS Get Started With Cybersecurity Prevention Plan |
How does blockchain for banking work?
Harvard Business Review claims that blockchain will do to banks what the internet did to media – revolutionize it. Blockchain has a number of characteristics that make it a must-have in the banking industry.
It is decentralized, transparent, secure, safe, and incredibly cheaper when compared to the traditional options available.
Blockchain archives and records all the transactions which take place in the network, thus eliminating the need for a third party for the brokerage.
It could provide specific financial services such as payments or securitization without requiring a bank.
The technology allows the usage of tools such as self-executing smart contracts which automate manual processes from compliance, claims processing, content distribution, etc.
It even disintermediates some of the key services that banks provide, such as fundraising, securities, loans and credit, clearance and settlement systems, payments, etc.
With blockchain technology, finance will change the way it operates- in a good way.
In this article, we are going to look at blockchain for banking applications, real examples of how some banks are leveraging blockchain technology, and the challenges that lie ahead.
Blockchain applications in the finance sector
Let us look at some of the blockchain applications in the finance sector that will disrupt the way financial institutions will operate.
1. Payments
Blockchain offers an inexpensive and secure way of sending payments which reduces the need for 3rd party verifications and reduces the processing time for bank transfers. All that is required is an internet connection.
The transactions are secure, mostly anonymous, and borderless. McKinsey estimates that blockchain-powered cross-border payments could save about $4 billion a year.
A merchant who doesn’t want to shell out the transaction fees from banks can instead take electronic payments from cryptocurrencies at a ridiculously low rate.
2. Secondary Market Trading
Purchasing a company’s shares requires clearing and settlement of trades. The ownership of the asset that is being traded must be verified and recorded. When there are a large number of orders, exchange fees and clearing fees will be a huge figure.
Let’s assume the ownership of shares exists on a blockchain and a change in ownership gets validated immediately, then it will reduce transaction costs and clearing costs by a long haul.
Also, it would apply to all sorts of asset classes- bonds, stocks, derivatives, commodities, real estate.
3. Know Your Customer (KYC)
Complying with anti-money laundering and Know Your Customer norms results in a lot of costs, and there can be no two ways about it when it comes to enforcing them.
Not only does this require a lot of time, but it also has to be performed manually.
Consumers lost $56 billion in 2020, with more than 49 million customers becoming identity fraud victims, per Javelin Research.
Performing due diligence reduces the chances of money laundering and fraud. Banks are mandated to upload the KYC data of a customer into a centralized database which is used to check the information of existing or new customers.
When you add blockchain for banking to the KYC equation, the verification process completed by one financial institution will be available for other banks as well.
There would be no need to duplicate the efforts, thereby proving a huge panacea to all financial institutions as it reduces the costs undertaken for this exercise.
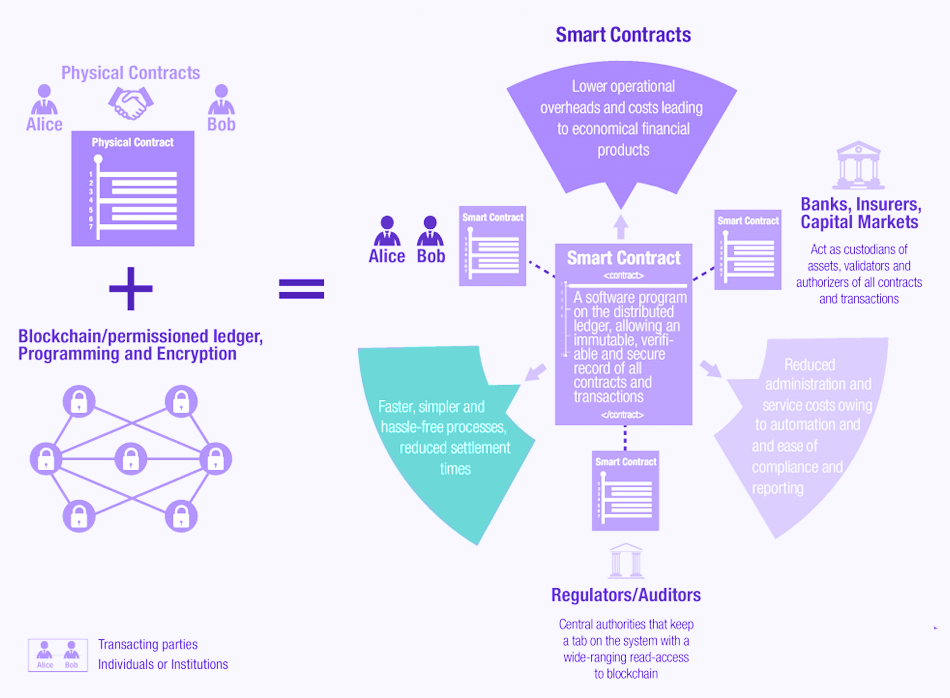
4. Smart Contracts
A smart contract is a self-governed piece of code that runs when certain conditions on it are met. When applied in the field of banking and financial institutions, it simplifies complex processes and speeds them up.
It will also ensure that the transaction gets approved only when accurate information has been input. Since the terms of the smart contracts are available to all the stakeholders, the possibility of errors during the time of execution is reduced drastically.
5. Fraud-Free Insurance Management
The efficiency of insurance claims increases manifolds with the help of blockchain for banking. The presence of smart contracts, access to customer information, decentralized customer authentication, ensure that the process of sorting huge volumes of insurance claims is done automatically.
Thanks to data-sharing across the industry, the instances of fraud claims reduce too.
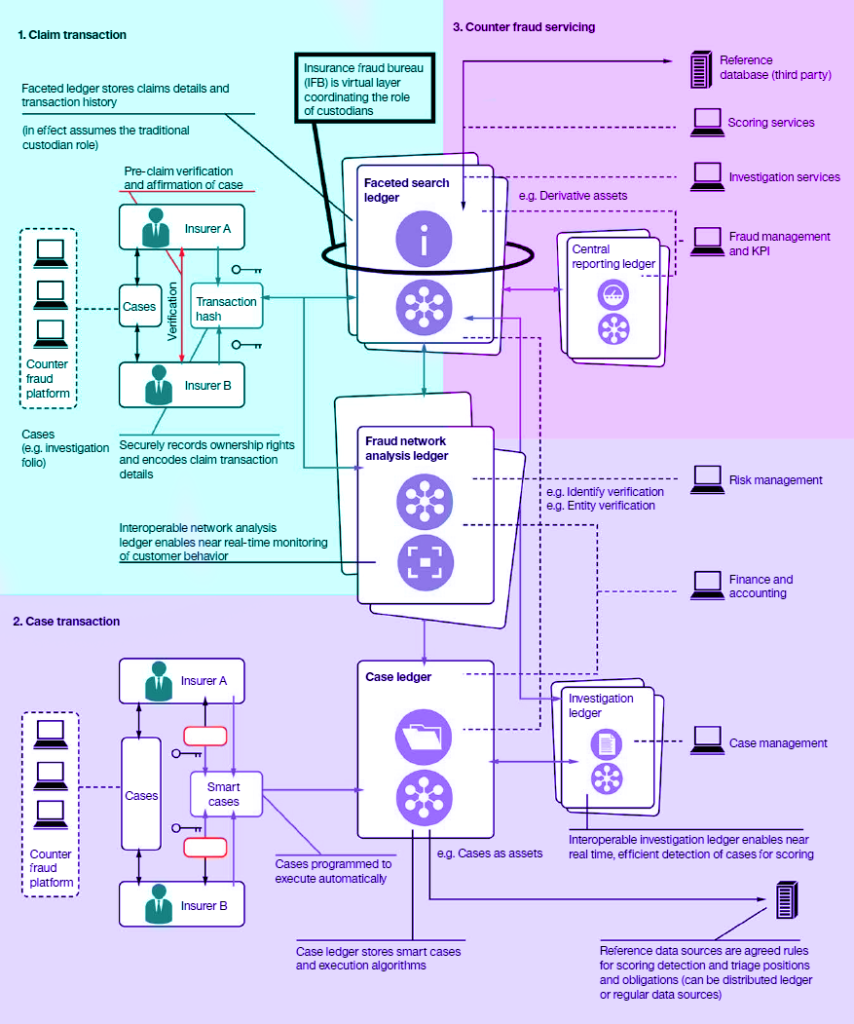
Thanks to blockchain’s potential for real-time transaction settlements, insurance companies will be able to introduce new risk instruments and exploit capital opportunities.
6. Clearance and Settlement Systems
The process of transferring money from one account to another involves a complicated system. It is a pain not only for the customer but also for the banks – it’s a logistical nightmare for the latter.
Let’s say you want to send money from an account of bank A in Germany to bank B in the US, the money transfer will be executed with SWIFT (Society for Worldwide Interbank Financial Communication).
If bank A and bank B don’t have a financial relationship, then the SWIFT number of a correspondent bank that has a relationship with both the banks is required and they take a fee for that.
The correspondent bank maintains different ledgers, at bank A and bank B as well, and they have to be regulated at the end of the day.
The SWIFT protocol only sends the payment orders, the actual money passes through a set of intermediaries which increases the cost of the transaction.
Blockchain technology can completely change this system. Instead of SWIFT, an interbank blockchain for payments could make the transactions public.
Instead of relying on a bunch of intermediaries and correspondent banks, transactions can be verified and settled on the blockchain itself.
7. Improving Securities Market
When you buy or sell assets such as debt, stocks, commodities, etc., there is a track kept of who owns what.
There is a chain of brokers, security depositories, exchanges, clearinghouses, and custodian banks which make this possible. The entire process is slow and inaccurate and there are chances of fraud too.
Once you buy the shares of a company, the shares are outsourced to custodian banks for safekeeping.
Since the buyers and sellers don’t use the same custodian banks, the custodians rely on a third party to hold the certificate of ownership papers. This system is inefficient and could be inaccurate too.
Securities transactions take anywhere from one to three days since everyone’s books have to be reconciled.
Since there are a number of parties involved, the transactions have to be manually verified. Also, each party charges a fee.
Blockchain technology creates a decentralized database of unique, digital assets. Thanks to the distributed ledger, it is possible to transfer the rights of an asset through cryptographic tokens.
Tokenized securities will be able to cut out middlemen like the custodian banks, thereby lowering the asset exchange fees.
8. Improved Lending
Blockchain-powered lending offers a much more secure way of providing personal loans to a large pool of consumers.
It also makes the loan process cheaper, secure, and more efficient. When you file your loan application, the bank will have to calculate the possibility of you not paying it back.
The banks look at factors such as debt-to-income ratio, credit score, home-ownership status, etc.
For this, the banks will have to approach credit agencies such as Experian, Equifax, and TransUnion to access your credit report. Using your credit report, banks will add the price of you defaulting on the loans to the interest.
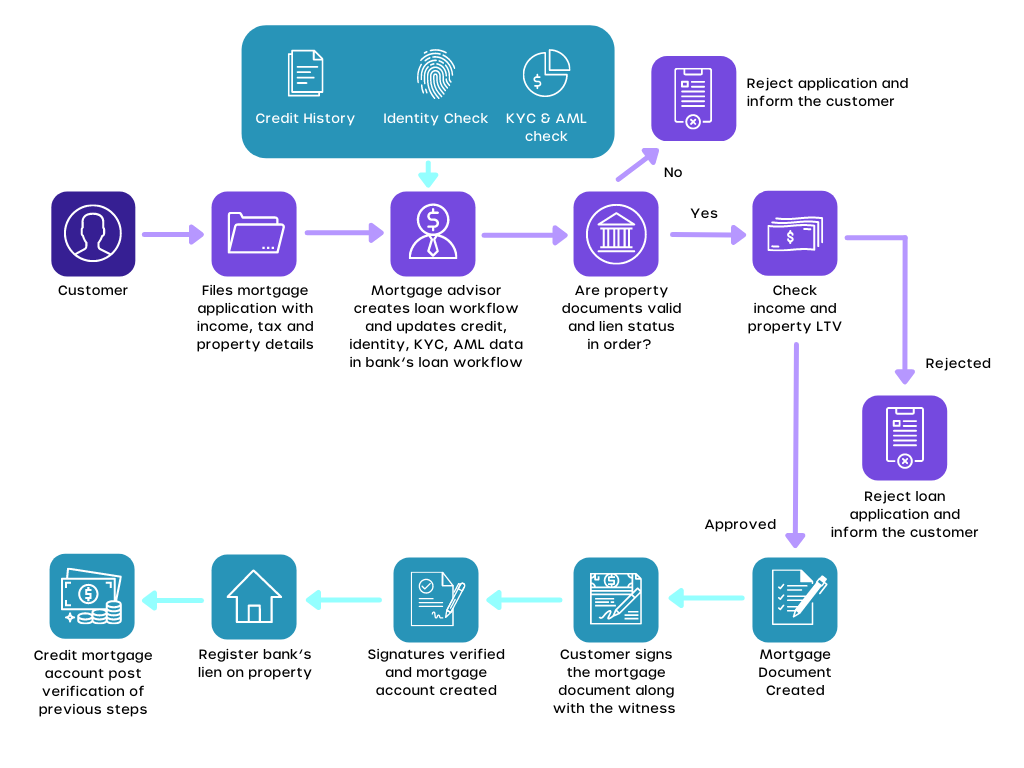
The blockchain-based lending process is smooth, efficient, and cost-saving
With a cryptographically secure and decentralized registry of historical payments, people can apply for loans based on a global credit score instead of relying on credit agencies.
Use Cases of Blockchain
Blockchain technology is a very promising technology of the 21st century and we will keep seeing new use cases as we understand it better and more platforms embrace its uniqueness & useability.
There are industries such as finance, insurance, and stock that could find immense value in the blockchain.
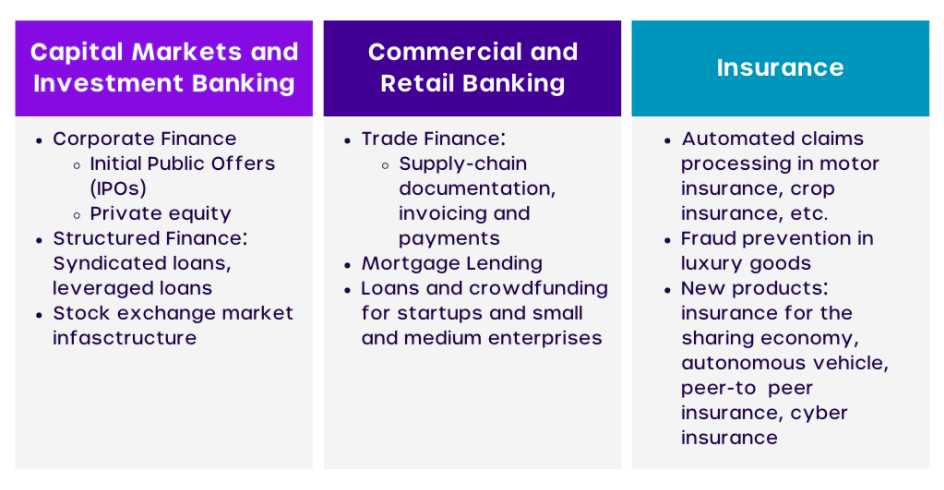
Examples of how some banks are using blockchain in financial services
- Westpac, one of Australia’s biggest banks partnered with Ripple, a blockchain-powered payment platform, to implement a low-cost cross-border payment system.
- HSBC and IBM successfully designed and tested an interoperable multi-ledger central bank digital currency that has securities and foreign exchange settlement capability.
- Nasdaq, the world’s second-largest stock exchange company, in partnership with Citigroup, invested into the blockchain ledger. It is a shared and trusted distributed database which records all transactions and changes in ownership, all of this in real-time.
- BNP Paribas, BNY Mellon, HSBC, ING, Natixis, and State Street support Fusion LenderComm by Finastra, a blockchain banking platform for syndicated loans.
- In 2018, PwC launched the first blockchain auditing service which will check how companies are using fintech blockchain.
- Circle, a decentralized app, allows P2P transfers for both cryptocurrencies (aka blockchain money) and fiat currencies.
What are the challenges in blockchain adoption?
While Blockchain for banking has a number of advantages, there are a few obstacles that will have to be overcome for financial institutions to leverage the technology to the hilt. Let us look at some of the challenges.
Privacy
Financial institutions have sensitive information as well as money stored with them, there is a lot that can go wrong.
Since the data stored on a blockchain are publicly available, the blockchain’s intrinsic anonymity nature doesn’t help much.
Banks should ensure that the data is kept securely and will not harm the customer in any way. Private blockchain for the banking sector is a must.
Accessing Encrypted Data
The data of an individual on the blockchain is securely encrypted with the help of a private key. If it is lost, then there is no way to recover it.
Ensuring Multiple Security Protocols
Thanks to the cryptographic techniques that it employs, the blockchain for banking networks is secure and powerful.
Cryptographic networks are extremely complex to hack and will require a huge amount of computational power to secure any hack.
When banks use blockchain networks, they have to be secured with a number of security protocols.
People in the organization should be given different layers of access to ensure that hackers don’t gain access to the network.
Scalability
The entries on the blockchain database will keep increasing as more and more organizations use it. It is a big challenge for the blockchain technology network.
When more and more entries are added, not only should blockchain be able to handle all the extra traffic, but also be able to maintain the access speed.
Legal Regulations
Banks will have to traverse through a number of regulations if blockchain for banking is applied. Without following the regulations, the banking sector will fall apart, and so will the trust that consumers have in these institutions.
Conclusion
Blockchain has found its use in the finance and banking sector and financial institutions are determined to find ways to implement it in their organizations. Disruption doesn’t happen overnight, and blockchain isn’t perfect yet.
That said, blockchain disruption is imminent and its impact has already started to be felt. The only question that remains is; are you going to be a part of this inevitable change?
Blockchain in the banking industry is expected to reach a market size of approximately $22.5 billion in 2026, from $0.28 billion in 2018. The incredible jump that you see in the market size is a testament to what is in store for blockchain in the banking and financial services industry.
| Orchestrate your cybersecurity tasks better Start a 30-day free trial of Cyvatar |