What are zero-day exploits and why are they dangerous?

What are zero-day exploits and why are they dangerous?
Cyvatar | 03/11/2022A developer managed to scrape data from Alibaba’s Chinese retail website Taobao, in November 2019. 1.1 billion users were affected and it was completely undetected for eight months.
LinkedIn, the world’s largest professional platform, was attacked by a hacker who exploited the site’s API. They scraped the data of 700 million users, or 90% of its user base, in June 2021.
Facebook, Yahoo, Apple, Microsoft, and many of the biggest tech giants in the world have been vulnerable to this.
What is it? It’s called a zero-day exploit
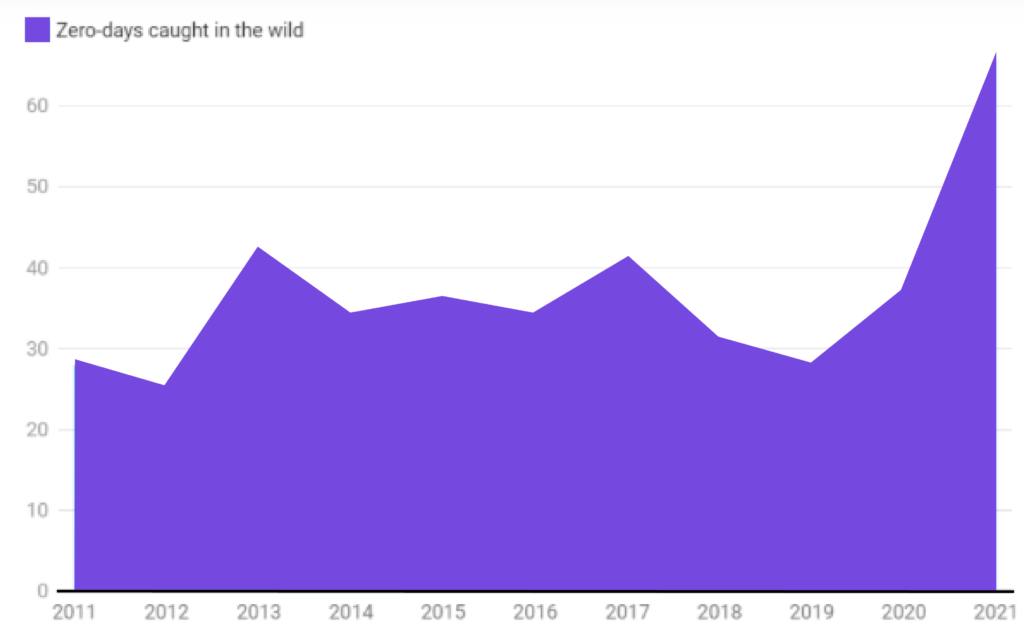
According to the Zero-Day Tracking Project, there were more than 83 zero-day exploits in the year 2021, that’s more than double that of 2020 (which had 36). Let’s dive deeper into what it is.
What is a zero-day exploit?
A zero-day (0day) exploit is a cyber attack that targets software vulnerabilities that are not known to the software vendor.
As soon as the attacker spots the vulnerability, it will quickly create an exploit and use it for the attack. Since the business is not aware of the vulnerability, it is difficult to defend it. That’s what makes zero-day exploits serious security threats.
According to Ponemon Institute’s Study on the State of Endpoint Security Risk, 80% of all successful data breaches in 2019 were a result of zero-day exploits. The above statistic is not at all surprising given the danger that zero-day exploits pose.
Who carries out zero-day exploits?
Cyber attackers are constantly on the lookout to exploit software vulnerabilities. There are many types of cyberattackers who have their own agenda.
⮞ Cybercriminals
These are attackers who have financial objectives to achieve through the exploits.
⮞ Hacktivists
These attackers have a social or political cause behind their attacks. They want to draw attention to the cause they are fighting for.
⮞ Corporate espionage
They spy on companies to gather information for gaining a competitive advantage.
⮞ Cyberwarfare attackers
They can be malicious non-state actors or state actors who want to compromise the cyberinfrastructure to create tensions.
Who are the victims of zero-day exploits?
A zero-day exploit can exploit vulnerabilities in multiple systems including office applications, consumer applications, web browsers, operating systems, open-source components, hardware and firmware, and the Internet of Things (IoT).
Individuals, businesses, and government agencies are the usual victims of zero-day exploits.
If you use computer systems every day, being a victim of zero-day attacks can pose serious risks as it infects the operating system, web browsers, applications, open-source components, hardware, etc., even through casual web browsing activities.
The activity could include opening a file or an email, clicking on a link, visiting a website, playing compromised media, and so on.
You can divide zero-day victims into targeted and non-targeted:
Targeted zero-day attacks- They are usually carried out against high-profile targets such as government agencies, powerful business enterprises, and important individuals.
Non-targeted zero-day attacks- They are carried out against vulnerable systems such as a business application or a web browser.
How to identify zero-day exploits?
A zero-day vulnerability can exist in the form of a broken algorithm, bugs, issues with password security, missing authorization, and so on.
On top of this, such vulnerabilities are hard to detect. Thanks to the nature of these vulnerabilities, most of them are detected only after the vulnerabilities have been exploited.
The following are some of the ways to detect zero-day attacks:
- Vulnerability Scanning
There are vulnerability scanning solutions that simulate attacks on software code to find vulnerabilities that could have been introduced after a software update. While this technique cannot detect all zero-day exploits, organizations need to act immediately after seeing the results of the scan.
A constant issue with most organizations is that they are usually late to respond to newly discovered vulnerabilities. On the other hand, cyberattackers will immediately latch on to any opportunity to attack.
- Zero-Day Initiative
There should be programs established specifically to reward people who find vulnerabilities in your system. It would be wise to have ethical hackers on board who can check for vulnerabilities at regular intervals.
- Incident Response Plan
If you want to mitigate the effects of a zero-day attack, then you are required to have a specific response plan in place.
You should have a strategy that will increase the chances of detecting zero-day attacks and follow a checklist of techniques to respond to zero-day exploits immediately.
- Windows Defender Exploit Guard
It is a security tool that comes with Windows 2010. The software comes with a host of capabilities to prevent zero-day exploits.
It can be used as your first level of security against zero-day attacks that target Windows.
- Next-Generation Antivirus (NGAV)
There is no doubt that traditional antiviruses are ineffective against zero-day exploits.
NGAV solutions use in-built technologies such as behavioral analytics, machine learning code analysis, threat intelligence, anti-exploit techniques, etc., that are highly effective against zero-day exploits.
- Patch Management
By establishing formal processes and implementing automated tools, organizations can understand which are the systems that require patching.
All they need to do is obtain the patches and deploy them immediately before attackers can make a move.
Why are zero-day exploits dangerous?
Zero-day exploits are extremely successful and severe since vulnerabilities are not immediately fixed by the organization.
Cybercrime attackers reserve their set of zero-day vulnerabilities for attacking targets of high value.
Financial institutions, government websites, and popular establishments are usually some of the main targets.
The biggest problem with zero-day vulnerabilities is that it doesn’t get resolved until the patch has been installed or the systems have been updated.
This takes a lot of time and most corporate admins fail to patch a zero-day vulnerability.
The operational, financial, reputational, and legal impact of zero-day exploits can be devastating.
Even if you don’t lose money, zero-day exploits are still devastating as they can go undetected for months, even years.
1. Steal financial data
Most cyber hackers enter the systems of financial institutions. While some of them sell the financial data to a third party, or on the dark web, some use the data for their needs.
Losing the money of customers will make it almost impossible to bring back a lost reputation.
2. Issues can be difficult to fix
When your system is compromised because of a zero-day exploit, it isn’t always easy to figure out where the problem stems from.
Since organizations use several disparate systems, locating the issue and patching the holes can be an arduous, if not an impossible affair.
3. Attackers can target your customers
If your products have many consumers, hackers could use them to breach the system to directly attack the customers.
4. They can threaten the company with consequences
Criminals can threaten you with Distributed Denial of Service (DDoS) and other attacks. DDoS is a cyber attack in which the criminals make the product or service unavailable to its users by disrupting services.
You certainly don’t want a DDoS attack as your paying customers will be unhappy and lose trust in your business if they cannot gain access to your product.
5. Zero-Day Attack Prevention
Since they can take many forms, it becomes a tad too difficult to protect yourself against zero-day exploits.
If the patch is not produced on time, then any type of software vulnerability could be exploited as a zero-day.
You might be wondering “What are the most recent zero-day attacks?” There are many recent zero-day attacks.
However, the most recent zero-day vulnerability named Log4shell took the Internet by storm.
Log4shell is a zero-day vulnerability that exploits the popular java logging framework called Log4j by logging data including user input leading to the unauthorized installation of code on the server.
Most software developers do not disclose the vulnerability as they hope to issue a patch before hackers discover it.
Here are a few strategies that you can adopt to prevent zero-day exploits:
- Update your systems
Developers should keep the systems updated at all times. Keeping the system continuously updated and patched reduces the possibility of exploitation.
Enable automatic updates so that it takes place routinely without manual intervention.
- Add additional security measures
Use powerful security solutions to reduce the chances of a severe attack.
Although you might not be able to prevent a zero-day exploit, your systems can at least be made strong enough to reduce the severity of the attack. Investing in a 24/7 monitoring and vulnerability management solution will help your business stay proactive with security vulnerabilities.
- Educate users within the organization
Without a doubt, most of the zero-day exploits become possible because of a stray human error.
Teach your employees and customers how to protect themselves and their data by following proper digital hygiene.
- Use only necessary applications
The more software in your organization, the more the vulnerability. Reduce the risk to your network by limiting the number of applications you use.
- Stay informed
Even though zero-day exploits aren’t publicized as it draws bad press if you hear a vulnerability about an application that your business uses, then put in extra security measures so that you can respond to threats. As your organization grows, cybersecurity awareness training is a smart investment to consider. Human error can lead to a breach.
It pays to keep yourself informed of the happenings in your industry.
Famous Zero-Day Attacks
Never underestimate the threats associated with a zero-day exploit. It is as dangerous and menacing for organizations as it is touted to be.
The attackers only need a minor loophole to exploit the environment. Let us look at some of the recent examples of zero-day exploits.
⮞ Apple: In 2020, a tiny bug in Apple’s iOS software allowed hackers to hack into devices remotely.
Described as one of the most secure among the software platforms, it fell prey to at least two sets of iOS zero-day vulnerabilities.
⮞ Microsoft Word: 2017 zero-day exploit compromised personal bank accounts. By opening a malicious Word document, the users were susceptible to the attack.
The document showed a “load remote content” requesting external access from another program. Once the victims press ‘Yes’, malware is installed on the device that captures their login credentials.
⮞ Stuxnet: Probably one of the most popular examples of a zero-day attack, it was first discovered in 2010, but dated back to 2005.
The worm affected manufacturing computers running programmable logic controller (PLC) software. It even made a documentary called Zero Days.
⮞ Zoom: In 2020, the world’s most popular video conferencing platform was attacked. This zero-day exploit involved hackers accessing a customer’s PC remotely, only if they had an older Windows version installed.
If an administrator was targeted, then the hacker could take over their entire machine and have access to all the files.
⮞ Sony: The zero-day exploit in 2014 brought Sony to its knees as it led to a vast repository of vulnerable files being made available on file-sharing sites.
The hacked data included business strategy, private email addresses of Sony executives, and details of forthcoming movies.
⮞ Operation Aurora: The intellectual property of several major enterprises such as Google, Adobe Systems, Dow Chemical, and Yahoo was exploited during this zero-day exploit.
Zero-Day Attacks Are Preventable With Cyvatar
Zero-day exploits are becoming increasingly common and even the most technologically empowered organizations are falling victims to it.
The most recent log4j vulnerability is a wake-up call. It calls for more active and fully managed security services.
| A proactive security strategy protects Cyvatar’s Fully Configured Secure Endpoint Management Members. If you are not a member and would like to try Cyvatar for your organization’s cybersecurity, SIGN UP for a FREE trial today at: https://clarity.cyvatar.ai/freemium. Or visit https://cyvatar.ai/membership-pricing to learn more about our monthly subscriptions. |