What is a risk management framework? | 7 steps to NIST RMF

What is a risk management framework? | 7 steps to NIST RMF
Cyvatar | 03/17/2022The Risk Management Framework by NIST is a set of guidelines that dictate how the US federal government organizations must be architectured, secured, and monitored to manage information security and privacy risks.
Originally developed by NIST in the NIST SP 800-37 document in 2010 to help organizations manage security and privacy risks, it also provides support for risk management programs to meet the requirements in the Federal Information Security Modernization Act of 2014 (FISMA).
RMF defines how people leverage processes to manage technology, governance, reporting, and responsibilities. It requires the right kind of planning, preparation, and analysis.
In this article, we will discuss the risk management framework, its components, steps to set up an RMF framework for your organization and understand its benefits.
Why Risk Management Framework?
Citibank wired a $900 million loan payoff to the cosmetic company Revlon’s money lenders, in 2020. This was done mistakenly. Citibank reached out to the hedge funds to return the money, some did, others refused.
Citibank decided to sue them. The federal judge ruled that Citibank can’t have its money back.
As you would imagine, Citibank had multiple controls and policies in place to ensure that mistakes like this won’t happen.
Initial reports said that the mistake could have happened because of compromised banking controls, but the problem was finally traced to a recently installed software that was rife with UI issues.
The software didn’t have appropriate controls and it led to the error. US regulators fined Citibank $400 million to update their data governance, risk management, and compliance controls.
This is where implementing a Risk Management Framework (RMF) becomes important for organizations. Citibank could have averted this situation had they implemented the RMF.
Five Risk Management Concepts
Breaking the risk management framework into different categories is helpful. It lets you provide a way of working towards an effective risk management system.
1. Risk Identification
One of the most important parts of the RMF is risk identification. According to NIST, the typical risk factors are vulnerability, threat, impact, likelihood, and predisposing conditions.
In this step, you must try to find the possible risks that you can imagine across all the systems and prioritize them based on different factors.
Examples of risks include operational risk, regulatory risk, legal risk, political risk, strategic risk, IT risk, and credit risk.
Once we have listed all the possible risks, the organization should divide them into core and non-core risks.
The risks that the company must take to ensure long-term growth and drive performance are considered core risks.
Non-core risks are those that are not necessary and can be left off.
2. Risk Measurement
It provides information on the size of the specific risk and the loss that could be incurred due to these exposures.
When organizations measure specific risk exposure, they need to consider the effect of that risk on the organization’s risk profile.
Additionally, businesses need to consider the possibility of measuring exposure. There are certain risks that are easier to measure than others.
3. Risk Mitigation
It involves examining the risks that have been identified and ascertaining that are the ones that should be eliminated. There are certain risks that are acceptable. Risk Mitigation can be achieved with the help of diversification, buying cyber insurance, hedging with derivatives, sale of assets, or sale of liabilities.
| Cyvatar’s fully managed services come with complementary cyber insurance – Cysurance |
4. Risk Reporting
The fourth component in the process is called risk reporting. It entails examining the risks regularly to ensure that the risk mitigation strategies that the organization has employed is giving good results.
It is important that the risk levels are regularly checked to ensure that they are at an optimal level. The risk reports must be sent to the risk personnel who have the authority to adjust risk exposures.
5. Risk Governance
The final component in the process is called risk governance. Governance makes sure that the risk mitigation techniques which have been employed are conducted according to the right strategies and that the employees are adhering to these policies.
Risk governance involves:
- Specifying the responsibilities of all employees
- Dividing duties daily
- Calculating risk limits
- Preparing risk reports
- Storing risks
- Checking for general oversight
- Delegating authority to committees, individuals, and the board for their approval
7 steps to NIST RMF
The NIST SP 800-39 rev 1 provides a 7-step risk management process instead of the previous six steps of the risk management framework, which helps align controls.
Instead of providing a one-size-fits-all approach, it addresses the risk of the diversity of components, systems, and custom environments.
An effective RMF builds security into systems and empowers the organization to address security concerns immediately.
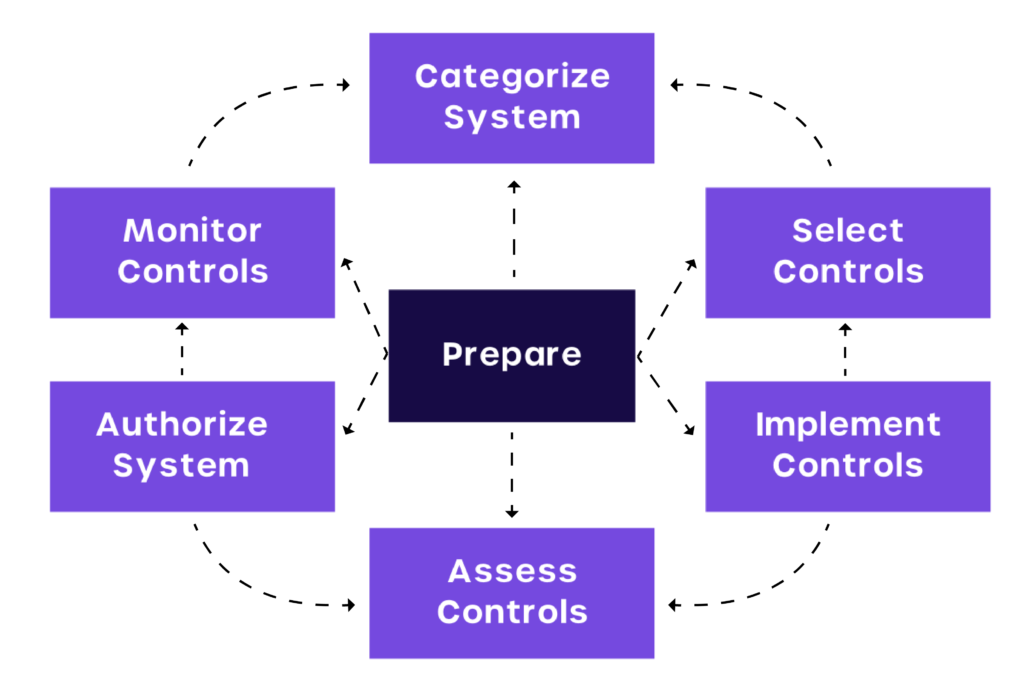
STEP 1: Prepare organizations to manage security and privacy risks
STEP 2: Categorize the system and information based on impact analysis
STEP 3: Select the set of NIST SP 800-53 controls to protect the system
STEP 4: Implement the security controls
STEP 5: Assess the effectiveness of the security controls
STEP 6: Authorize risk-based decisions
STEP 7: Monitor Security Controls
Let us look at each of these steps in detail.
STEP 1:
This step is a new addition in NIST SP 800-39 revision 2 acknowledging the importance of preparing the organization to get the most out of RMF, primarily focusing on communication.
It prepares the organization to execute the RMF by establishing a context and priorities for managing privacy and security risks at the system and organizational levels.
What to Expect:
| -⮞ Identification of key risk management roles -⮞ Determination of risk tolerance, establishing risk management strategy -⮞ Organization-wide assessment of risk -⮞ Development and implementation of organization-wide strategy for continuous monitoring -⮞ Identification of common controls |
STEP 2:
Use NIST standards to categorize information and systems to get accurate risk assessment of these systems.
NIST tells what kind of systems and information should be provided and the level of security that is required to implement based on the categorization.
Prepare by taking an inventory of all the data that resides in your environment. It is imperative that you identify sensitive data that is open to unauthorized users and data that is of no value at all operationally.
Additionally, you will also have to write down the intended use of each systems’ operation and how they are connected with each other.
What to Expect:
| -⮞ Documentation of system characteristics -⮞ Completion of security categorization of the system and information -⮞ Review/Approval of categorization decision by authorizing official |
STEP 3:
The next step is to select the relevant controls for your system based on NIST Special Publication 800-53 and FIPS 200.
These security controls will facilitate a consistent, compatible, and repeatable approach for selecting and specifying security controls for systems.
The controls will vary from one system to the next. It could include anything from adopting monitoring solutions to shaping policies that will reduce your risk concerns.
Make sure that you restrict access to sensitive information by reviewing who is given access. Eliminate unused or empty groups or those that have non-expiring passwords.
What to Expect:
| -⮞ Selection and tailoring of control baselinesDesignated controls as a system-specific, hybrid, or common -⮞ Allocation of controls to specific system components -⮞ Development of system-level continuous monitoring strategy |
STEP 4:
The organization will have to put security controls in place to measure and benchmark its position. The policies should be specific and in line with cybersecurity framework initiatives.
Train your staff on day-to-day management, reporting, directory management, and user permissions. Identify where the most important data for your organization lies and keep monitoring who has access to it.
Confirm data owners and monitor new folders that require access and remove unnecessary access.
If there are unusual patterns of access, make sure you investigate them immediately. If important files are accessed from a new IP address, then you need to monitor them.
Implement security controls and elaborate on how the controls are employed within the information system. The policies should be customized to each device for accessing security controls.
What to Expect:
| -⮞ Implementation of controls specified in security and privacy plans -⮞ Update of security and privacy plans to reflect controls as implemented |
STEP 5:
It involves the usage of appropriate assessment procedures. The security controls will determine the extent to which they can be implemented.
The organization should be in a position to respond to potential security risks immediately.
One of the most important things to maintain security is automation. Benchmark your security controls using assessment procedures and determine if the controls that are implemented produce the desired outcome.
What to Expect:
| -⮞ Selection of assessor/assessment team -⮞ Development of security and privacy assessment plans -⮞ Approval of assessment plans -⮞ Conduction of control assessment in accordance with assessment plans -⮞ Development of security and privacy assessment reports -⮞ Remediation actions are taken to address deficiencies in controls -⮞ Updation of security and privacy plans to reflect control implementation changes based on assessments and remediation actions -⮞ Development of a plan of action and milestones |
STEP 6:
This stage is based on the determination of the risk to the organization’s assets, operations, individuals, and information systems.
The organization should implement authorized data workflow and policy if there is any untoward incident.
They should be prepared to enforce the policy by correcting any deviations so that they can be returned to a trusted state.
They also have to make sure that the data that was affected as a part of the incident is protected by archiving, deleting, and migrating it to a safer alternative location.
At this stage, the leadership team should make sure that the risk mitigation strategies put in place are working.
They should also ensure that the strategies adhere to all the applicable laws and policies within the organization.
What to Expect:
| -⮞ Authorization package -⮞ Rendering of risk determination -⮞ Providing risk responses -⮞ Approval/Denial authorization for the system or common controls |
STEP 7:
Continuously monitoring security controls allows the organization to maintain the security authorization of an information system.
The enterprises have a highly dynamic operating environment and the systems are always susceptible to vulnerabilities, threats, technology changes, and business process changes.
By monitoring security controls via automation, the organization’s cyber hygiene is maintained and monitored. The RMF insists on continuous monitoring.
If there is a change in the security status, a review of the authorization should be initiated immediately.
What to Expect:
| -⮞ Monitoring system and environment of operation in accordance with the continuous monitoring strategy -⮞ Ongoing assessments of control effectiveness in accordance with the continuous monitoring strategy -⮞ Analysis and response to the output of continuous monitoring activities -⮞ Reporting security and privacy posture to management -⮞ Conducting ongoing authorizations based on the results of continuous monitoring activities |
Benefits of Risk Management Framework for Businesses
RMF was initially developed for federal organizations, to make their systems become risk-free.
Private businesses and non-profit organizations have found that implementing RMF is extremely beneficial to their organization.
It can help the organization reduce its risks, minimize legal exposure, and maximize profitability.
Now that we have a better understanding of what RMF entails, let us look at how organizations can benefit from it.
- Reputation Management
Risk management should be implemented by different players in the organization- management, suppliers, and board members.
All of them should play an active role in mitigating risks. Having a strong risk management framework allows organizations to monitor news sources in real-time.
It can also help companies analyze gaps in controls and develop a strategy to reduce reputational risks.
- Supply Chain Risk
The global supply chain is extremely complex and requires constant monitoring to ensure that the risk is mitigated.
RMF optimizes the data management process and allows for better monitoring and connects different types of information from a number of sources and provides it in a single place.
- Competitor Analysis
Use different channels of information such as blogs, social media, news, podcasts, webinars, etc, to gain insights about your competitors.
Through RMF, organizations will have the capability to react quickly to what competition does and they will be better placed to come up with relevant strategies.
- IP Protection
All companies are exposed to potential intellectual property theft. A risk management framework allows organizations to protect themselves against potential losses of business opportunities, legal risks, and even competitive advantage.
- Asset Protection
A solid RMF understands the risks that are taken to protect an organization’s assets.
Thanks to its semantic technology, RMF presents unstructured data in a format that allows for easy understanding and retrieval.
- Better Privacy Controls
RMF helps the organization outline privacy controls so that they work in compliance with the local government’s laws and policies.
It also defines measurable policy requirements for the information systems. Implementing RMF helps you build a base for your organization’s privacy.
You will have a comprehensive defense against external and internal threats by leveraging RMF in your organization.
Risk Management Framework as a Culture
Don’t be driven by RMF as a compliance measure, rather think of it as a central pillar that holds your security intact.
It offers you a host of operational benefits.
NIST RMF and other security regulations have the following areas in common:
- Identifying your at risk data and systems
- Protecting the data and minimize the risk surface
- Monitoring and detecting on what’s happening on data
Cyvatar’s advanced AI system enables organizations to manage and automate most of the recommendations by NIST SP 800-39 that RMF offers.
Talk to one of our cyber experts now to learn more about our fully-managed cybersecurity services.